Fostering Women Entrepreneurship and Empowerment in Rural India: The Role of Ecosystem

Written By: Shivani Narang, National Partnership Officer at Humana People to People India,
Co-authored with Manu Mayank, Head – Social Impact & Sustainability at Humana People to People India
In the dynamic landscape of entrepreneurship, every individual embarks on a journey marked by both challenges and opportunities. It’s a journey fueled by traits like resilience and determination—qualities that serve as the bedrock for venturing into economic security. Yet, for rural women, this journey is often laden with additional obstacles stemming from societal norms and policy limitations. However, with the right support system, these obstacles can be transformed into stepping stones toward success. Ecosystem development is not just about providing resources; it’s about creating a nurturing environment where women can thrive.
Enter the concept of ecosystem development—a holistic approach aimed at fostering an environment conducive to women’s entrepreneurship and empowerment. It encompasses a range of enablers, from equitable access to finance, infrastructure, and markets to fostering a supportive culture within families and communities. Women must harness tailored education and training programs to unlock their entrepreneurial potential, advocate for policy changes, and leverage networking opportunities. As this ecosystem flourishes, it profoundly impacts women’s entrepreneurship development, catalysing economic opportunities, empowerment, job creation, and local economic growth. Ultimately, by nurturing the individual characteristics of rural women and fostering a supportive ecosystem, we pave the way for a more inclusive and prosperous future.
In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the importance of supporting and nurturing women entrepreneurs in rural India. These women often encounter numerous challenges when initiating and expanding their businesses, including limited access to resources, lack of education and training, low digital and financial literacy, and societal expectations. However, with the establishment of the right support structures and infrastructure, rural Indian women have the potential to not only succeed as entrepreneurs but also drive economic and social change within their communities.
Ecosystem development is pivotal in creating an enabling environment for women’s entrepreneurship and economic security. A supportive ecosystem for women entrepreneurs involves diverse stakeholders, including government agencies, non-profit organisations, corporations, financial institutions, and educational and skill-building institutions. Through collaborative efforts, these stakeholders can provide women entrepreneurs with the resources, networks, and mentorship necessary for success.
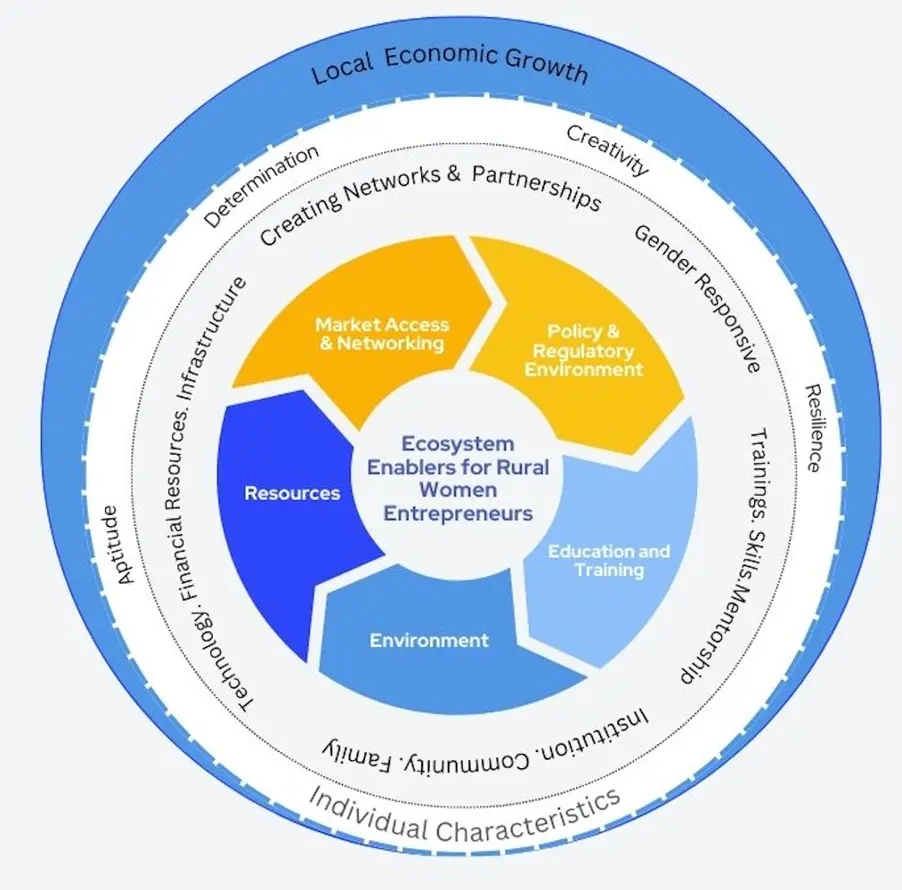
Local Entrepreneurship Ecosystem Development (LEED) concept visualisation
Access to finance is a crucial aspect of ecosystem development for women entrepreneurship. Many rural Indian women lack the collateral or financial literacy required to access traditional forms of financing. By offering microcredit, financial literacy training, and facilitating access to government schemes and grants, women entrepreneurs can overcome these barriers and realise their business aspirations.
Capacity building and skill development are also vital components of ecosystem development. Many women entrepreneurs in rural India need more skills and knowledge to run a successful business. Training programs, workshops, and mentorship opportunities can empower women to build the confidence and expertise needed to navigate the challenges of entrepreneurship.
Networking and mentorship are equally essential in ecosystem development for women entrepreneurship. By connecting women entrepreneurs with experienced mentors, peers, and potential collaborators, women can access invaluable support, guidance, and opportunities for growth. Networking events, conferences, and online platforms further provide visibility and connections necessary for scaling businesses.
In addition to the challenges of accessing resources and building supportive ecosystems, rural women entrepreneurs often face significant cultural and social barriers that hinder their ability to pursue entrepreneurship.
Traditional gender roles, cultural stigmas surrounding women working outside the home, and lack of support from family members or community leaders can all pose formidable obstacles. Addressing these barriers requires targeted interventions that are culturally sensitive and community-driven. Initiatives such as community outreach programs, educational campaigns to challenge gender stereotypes, and efforts to promote gender equality and women’s rights at the grassroots level are essential. By acknowledging and addressing these cultural and social barriers, we can create a more inclusive and enabling environment for rural women entrepreneurship, allowing them to fully realise their potential and contribute meaningfully to their communities economic and social development.
Together, let us cultivate a supportive ecosystem that empowers rural women to pursue their entrepreneurial dreams, creating a brighter future for themselves and their communities.
